What Is Pcos?
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder in women of reproductive age. It is a condition that can affect the menstrual cycle, fertility, hormones, and aspects of appearance.
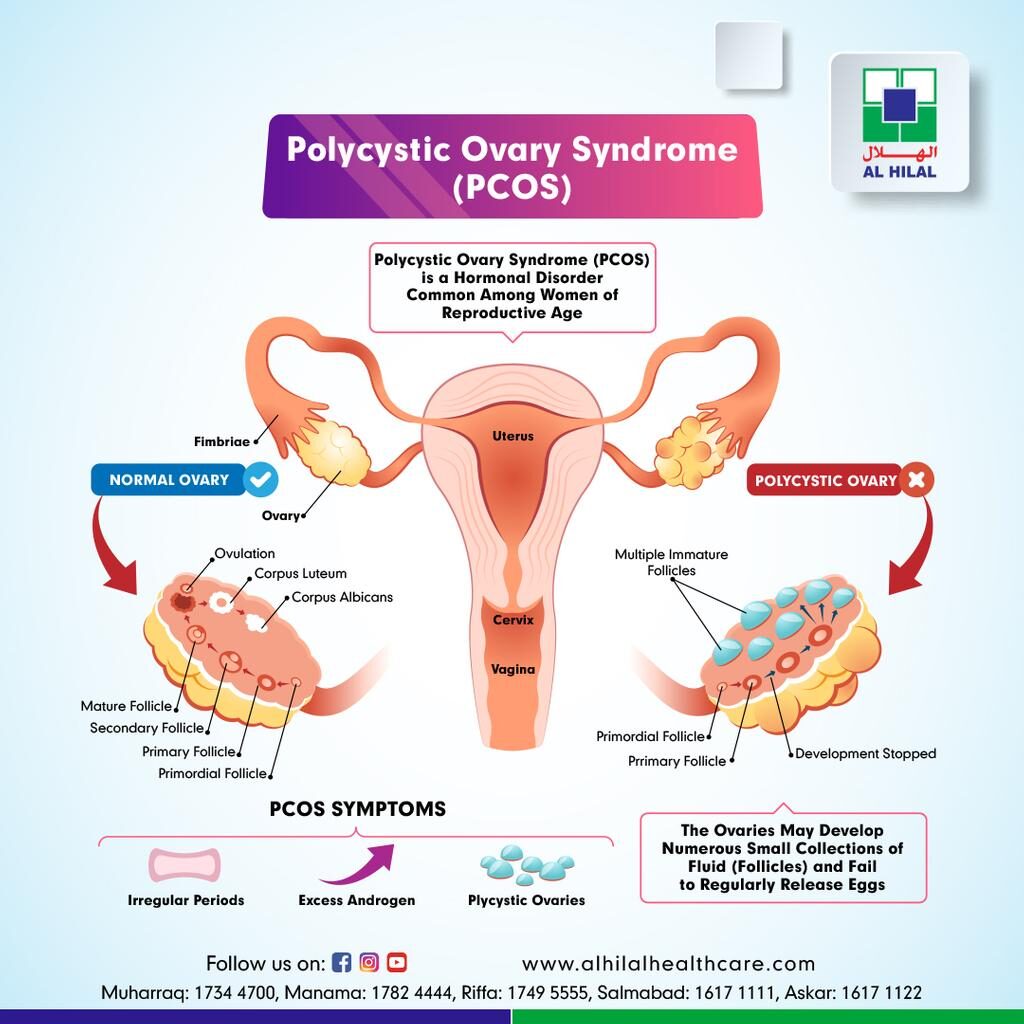
What Are Polycystic Ovaries?
Polycystic Ovaries are slightly bigger than usual and characterized by the presence of fluid-filled tiny sacs (cysts) in the ovaries. Having polycystic ovaries on an ultrasound scan doesn’t necessarily mean that you have PCOS.
PCOS V/S PCOD:
What is the difference between “Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Polycystic Ovarian Disease?” is a common question that disturbs many women.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is an endocrine system disorder, whereas Polycystic Ovarian Disease is a medical condition because by hormonal imbalance.
- Both PCOD and PCOS form cysts in your ovaries.
- In PCOS, large ovaries are made out of immature eggs and other secretions, causing irregular periods. PCOD, on the contrary, has similar implications on the ovary; they are minor.
- In PCOD, periods are regular, sometimes delayed. It is detected when a woman of childbearing age cannot conceive.
- There is a difference between PCOD and PCOS when getting pregnant naturally. You can conceive much more quickly in PCOD as compared to PCOS.
For Health Related Inquiries Please Contact
Symptoms Of Pcos:
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Excess body hair, especially on the chest, face, stomach, and back
- Increase in weight or difficulty in losing weight. As many as 4 in 5 women with PCOS are obese.
- Acne may persist beyond the standard teenage years
- Oily skin
- Thinning of scalp hair or hair loss
- Dark skin around the neck, elbows, and armpits
- Difficulty in getting pregnant
Symptoms typically begin in the late teens or early twenties. However, these symptoms differ from woman to woman. Some have very few symptoms, while women with severe PCOS can have marked hair growth, infertility, and obesity.
Causes Of Pcos:
There is no definite cause for PCOS, and several factors probably get in with it.
Insulin resistance: Insulin is the hormone that controls the level of sugar in the blood.
In PCOS, the body may not respond to insulin, so the level of glucose (a type of sugar) is higher. To prevent the glucose levels from becoming higher, the body produces even more insulin. Elevated insulin levels can lead to weight gain, irregular periods, fertility problems, and higher levels of testosterone hormones.
Hereditary factors: PCOS is not generally inherited from parents, but it may happen in some families. There seems to be a genetic factor involved in some cases, but this is not yet understood.
Health Risks Of Pcos:
While PCOS is a relatively harmless condition, secondary health problems may arise. Some complications of PCOS are:
- Infertility
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes
- Preeclampsia
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver
- Sleep Apnea
- Depression and eating disorders
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Endometrial and cervical cancer
How Can Pcos Be Diagnosed?
Having polycystic ovaries on an ultrasound scan doesn’t mean you have PCOS.
Medical history, examination, blood tests, and ultrasounds diagnose PCOS.
PCOS is diagnosed through an ultrasound to check for cysts and blood tests to examine androgen and other hormone levels.
Treatment For Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome:
Treatment is adjusted for each woman according to symptoms, other health problems, and whether she wants to get pregnant. It also depends on your age and symptoms.
- First-line treatment is diet change and activity; a healthy diet and weight loss are one of the best ways to manage PCOS.
- For overweight women, weight loss alone may regulate the menstrual cycle. However, even a slight loss of weight may help make menstruation more regular. Losing weight also has been found to improve cholesterol and insulin levels and relieve symptoms such as excess hair growth and acne.
- Medications targeting ovulation and insulin resistance are also recommended to aid in alleviating other symptoms of the disease.
- Insulin-sensitizing drugs used to treat diabetes are frequently used to treat PCOS. This is because these drugs help the body respond to insulin.
- Women with PCOS can help decrease androgen levels and improve ovulation. In addition, restoring ovulation may help make menstrual periods regular and more predictable.
- Successful ovulation is the first step toward pregnancy. For women who are overweight, weight loss may accomplish this objective. Medications can also be used to cause ovulation. Surgery on the ovaries has been used when other treatments do not work.
How Does Diet Affect Pcos?
People with PCOS are often found to have higher insulin levels than normal. Too-high insulin levels can cause your ovaries to produce more androgens, like testosterone. In addition, a diet high in refined carbohydrates, like starchy and sugary foods, can make insulin resistance and weight loss more difficult to manage. High-fiber foods can help combat insulin resistance.
Diet Modification:
- Cut down the calories, especially in the evening
- Spread the calories throughout the day by having 5 to 6 small meals
- Sufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D
- Consume food rich in Zinc
- Eat food that contains chromium like broccoli, whole wheat bread, and grape juice
- Minimize whole-fat dairy products such as whole milk butter
- Cholesterol level should be less than 300 mg daily
- Adapt low-fat cooking methods like baking, grilling, and boiling rather than frying.
For Health Related Inquiries Please Contact
Lifestyle Modifications:
Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle in PCOS are associated with ovulation and failure of infertility treatment. Weight reduction includes a combination of increased physical activity, caloric restriction, and behavior modification.
The following are some of the Lifestyle changes to manage PCOS:
- Manage a healthy weight
- Have regular health checks
- Keep your stress in check with meditation and yoga
- Exercise daily
- Quit smoking
Pcos Treatment In Bahrain:
Al Hilal Hospital is the largest and fastest-growing chain of private healthcare providers in Bahrain, with five branches. Al Hilal Healthcare Group is committed to providing high-quality healthcare services at an affordable price to the people of Bahrain through a combination of superior medical technology and excellent clinical services. Its vision is to be the largest healthcare service provider in the region by catering to the needy at the most affordable rates.
The Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology has been providing comprehensive healthcare for women. As a result, the healthcare group has successfully treated many PCOS patients and has given them a new life.
Pcos Specialist In Bahrain:
Al Hilal Healthcare group is equipped with several well-qualified and experienced Gynecologists who are specialists in treating PCOS.


