Pneumonia is a condition of acute respiratory disease that affects the lungs. It is an inflammation of lung parenchyma generated by an infectious agent. The lungs are composed of tiny sacs called alveoli, which replenish with air when a healthy individual breathes. When a person has pneumonia, the alveoli are filled with fluid and pus, limiting the oxygen intake.
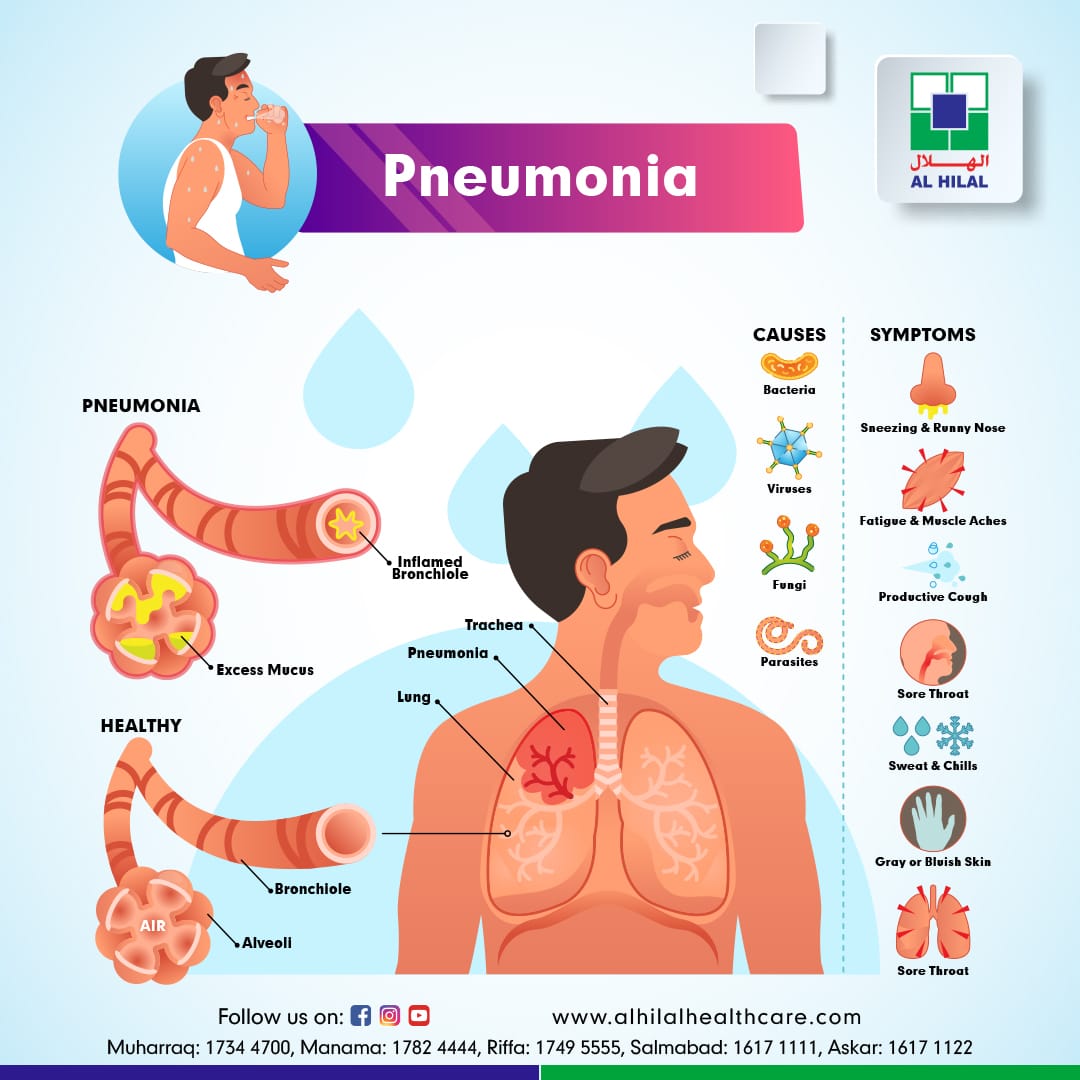
Pneumonia can vary in severity from gentle to life-threatening. It is most severe for young children and infants, people older than 65, and people with health problems or weakened immune systems. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Both bacterial and viral pneumonia is contagious. This means pneumonia can transfer from one person to another by inhaling airborne droplets from a cough or sneezing. You may also get these types of pneumonia by contacting surfaces or objects contaminated with pneumonia-causing bacteria or viruses.
Pneumonia is classified according to how or where it was acquired:
- Hospital-acquired Pneumonia (HAP) – This bacterial pneumonia is received during a hospital visit or stay. This is the most severe type of pneumonia, as the bacteria may be more resistant to antibiotics.
- Community-acquired Pneumonia (CAP) refers to pneumonia acquired outside a medical or institutional setting.
- Ventilator-associated Pneumonia (VAP) – When people using a ventilator get pneumonia, it’s called VAP.
- Aspiration Pneumonia – Inhaling bacteria into your lungs from food, drink, or saliva can cause aspiration pneumonia. It’s more likely to occur if you have a swallowing problem or are under sedation from medications, alcohol, or other drugs.
SYMPTOMS OF PNEUMONIA:
The following are the common symptoms of pneumonia:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Cough
- Rapid heartbeat
- High temperature
- Feeling generally unwell
- Sweating and shivering
- Loss of appetite
- Chest pain, which gets worse when breathing or coughing
The following are the less common symptoms:
- Coughing up blood
- Fatigue
- Wheezing
- Feeling sick or being sick
- Joint and muscle pain
- Headache
- Feeling confused and disorientated
CAUSES OF PNEUMONIA:
Pneumonia is generally the result of a bacterial infection. The other causes of pneumonia are:
- Aspiration Pneumonia – Aspiration pneumonia is caused by breathing an alien object, such as a peanut, or a harmful substance, such as a chemical or smoke.
- Viral pneumonia – is caused by a virus, such as a corona virus.
- Fungal Pneumonia – This is more likely to affect people with a weakened immune system.
DIAGNOSIS OF PNEUMONIA:
Your doctor will examine your medical history, perform a physical exam, and order diagnostic tests such as a chest X-Ray and sputum examination to diagnose pneumonia. This data can assist in determining what type of pneumonia you have.
One or more of the following tests are done by your provider if they think that you have pneumonia:
- A Chest X-Ray is done to look for lung inflammation. This is the most used method to diagnose pneumonia.
- Blood Tests, such as a CBC, check whether your immune system is combating an illness.
- Pulse Oximetry calculates the amount of oxygen in your blood. Pneumonia can keep your lungs from acquiring enough oxygen into your blood. A little sensor called a pulse oximeter is attached to your ear or finger to estimate the levels.
If you are in the hospital, are older, have severe symptoms, or have specific other health problems, your doctor may ask you to do further tests to diagnose pneumonia.
- If you are very sick, a blood gas test may be done. This test measures blood oxygen levels using a blood sample from an artery, usually in your wrist. Thus, this is called an arterial blood gas test.
- A sputum test may be used to discover what germ is causing your pneumonia.
- A blood culture test can determine the germ causing your pneumonia and show whether a bacterial infection has extended to your blood.
- A Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test matches your blood or sputum specimen to discover the DNA of germs that cause pneumonia.
- A Bronchoscopy looks into your airways. If your therapy is not working well, this process may be needed. At the same time, your doctor may also collect samples of your lung tissue and fluids your lungs to find the reason for your pneumonia.
- A Chest Computed Tomography Scan can show how much of your lungs are affected by pneumonia. It can also indicate whether you have complications such as lung abscesses or pleural disorders. A CT scan shows more detail than a chest X-ray.
- A pleural fluid culture can be taken using a procedure called Thoracentesis, when a doctor uses a needle to take a fluid sample from the pleural space between your lungs and chest wall. The fluid is then tested for bacteria.
PREVENTION OF PNEUMONIA:
Preventing pneumonia in children is a crucial method of reducing child mortality. Immunization against measles, Hib, pneumococcus, and whooping cough is the most helpful method to prevent pneumonia.
Adequate nutrition is vital to improving children’s natural protection, starting with exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life. In addition to preventing pneumonia, it also helps reduce the length of the illness if a child becomes sick.
Managing environmental factors such as encouraging good hygiene in crowded homes and avoiding indoor air pollution also lowers the number of children who fall sick with pneumonia.
TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA:
Mild pneumonia can generally be treated at home by taking adequate rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking antibiotics after consulting a physician. However, severe cases of pneumonia may require admission to the hospital.
You should always complete taking a stipulated period of antibiotics, even if you feel better unless a doctor tells you otherwise.
If you cease having an antibiotic part way through a course, the bacteria can become invulnerable to the antibiotic.
After starting the treatment, your symptoms should improve.
However, how fast they improve will depend on your pneumonia’s severity.
THE EFFECTS OF PNEUMONIA ON THE BODY:
Pneumonia is an illness in one or both lungs. Viruses and bacteria are the most common reasons for pneumonia. However, fungi can cause pneumonia, as well. The disease generates inflammation in the air sacs of the lungs. This results in a buildup of fluid that renders it hard to breathe. Pneumonia can be a medical emergency, particularly among high-risk groups like people over 65 and children of five or younger. It can also lead to sepsis, infection in the blood, multi-organ dysfunction, respiratory failure, and even death if not treated properly.
RED FLAG SIGNS:
- Tachypnea (Respiratory rate > 40 breathes 1′)
- Low oxygen
- Low blood pressure
- Difficulty in breathing/abnormal breathing
- Altered level of consciousness
- Chest pain
- Coughing out blood
TREATMENT OF PNEUMONIA IN BAHRAIN:
Al Hilal Hospital is Bahrain’s largest and fastest-growing chain of private healthcare providers, with five branches. Al Hilal Healthcare Group is committed to providing high-quality healthcare services at an affordable price to the people of Bahrain through a combination of superior medical technology and excellent clinical services. Its vision is to be the largest healthcare service provider in the region by catering to the needy at the most affordable rates.
The Department of Internal Medicine in Al Hilal has provided comprehensive and quality healthcare for adults for an extended period. All the facilities for the treatment of pneumonia are available in Al Hilal at an affordable cost.
SPECIALIST IN TREATING PNEUMONIA IN BAHRAIN:
Al Hilal Healthcare group is equipped with several well-qualified and experienced Internal Medicine physicians who are specialists in treating pneumonia and other internal organ illnesses.


