Caesarean is defined as an operation performed to deliver the baby through the abdominal route when vaginal delivery is impossible. It is also employed to speed up the delivery when potential danger to either mother or baby is anticipated.
The most common reasons to opt for a Caesarean delivery are:
- When there is a disproportion between the baby’s size and the maternal pelvis, there can be difficulty in the baby passing through the birth canal.
- If the mother has previously delivered by cesarean.
- If the mother has undergone the previous
surgeries in her womb, it is safer to go by cesarean as vaginal delivery can stress the uterine scar, and it may give away, which is life-threatening to both mother and baby.
- If the pregnancy is complicated by severe hypertension or the mother develops vaginal bleeding during labor.
- If the baby’s heart rate starts dipping below normal during labor, doing a cesarean can save the baby without losing more time.
One of the main advantages of this mode of delivery is that it does not require any effort from the mother. Hence it’s always the fear in her regarding the outcome of delivery. It also puts out the fear of pain, which is the most dreaded accompaniment of normal delivery, though nowadays, painless labor is widely employed in most hospitals.
But Caesarean section comes with its disadvantages. First, the mother has to undergo surgery instead of going through the natural process of vaginal delivery. That, in turn, results in a delayed healing process. She may also have to undergo a repeat cesarean the next time, increasing surgery-related complications.
Caesarean can also lead to surgical complications like excessive bleeding, infection, and anesthesia-related complications like any other surgery. In addition, the surgery can also cause injury to nearby organs like the urinary bladder and intestines.
Moreover, babies born by Caesarean are at a higher risk of having “respiratory distress syndrome” at birth.
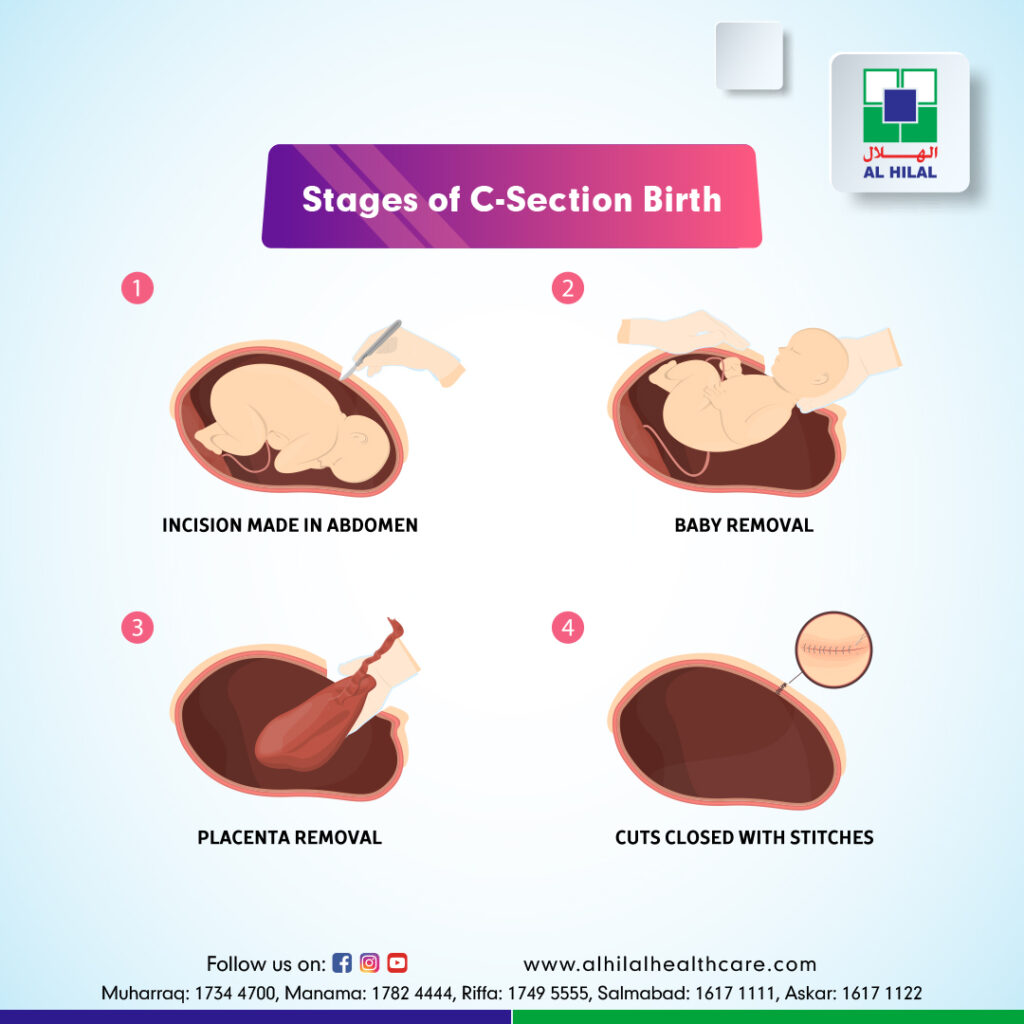
Steps of Cesarean Section:
After anesthesia, the patient is positioned, and the abdomen is cleaned with an antiseptic solution and draped. A skin incision of about 10 cm is made over the lower abdomen. The underlying layers of fat and muscle are cut and retracted till the uterus is reached. A cut is made on the uterus, and the baby is delivered. This is followed by removing the placenta, and the uterine wound is stitched. The abdomen is stitched in layers.
Postoperative Recovery:
The average hospital stay after a cesarean is 3-4 days. The mother is kept on a light diet for the first two days of the hospital stay. A regular diet is started once she has passed stools. In the postoperative period, it is important to start moving around as soon as possible, as total inactivity can result in severe complications like the development of blood clots.
After the anesthesia starts wearing off, the patient is given a sufficient dose of painkillers for pain relief. The mother is encouraged to be with the baby and breastfeed every 2 hours and on-demand. A urinary tube is placed during surgery and up to 12 hours after for continuous urine drainage.
It is essential to have adequate hydration during this period to enhance milk production and prevent urinary tract infections.
Once the mother is discharged, and back home, she should prioritize her diet, activity, and personal hygiene. A nutritious diet consisting of pulses, fruits, and nuts will speed up her recovery and boost the quality and quantity of breast milk. In addition, she should not restrict herself to bed but move about engaging in routine activities. Strenuous activities like lifting weights should, however, be avoided.
The wound should be cleaned and kept dry. An antibiotic ointment may be applied over the wound for one week. Pain may persist for a variable duration for which painkillers can be taken as prescribed by the gynecologist. It takes about six weeks for complete recovery.
However, one should not ignore symptoms like fever, severe abdominal pain, excessive vaginal bleeding, pus discharge from the wound, and shortness of breath and should visit the gynecologist immediately.
Nowadays, though Caesarean is highly safe surgery, one should be aware of the long-term risks. Therefore, an elaborate discussion with the gynecologist will help one make an informed decision regarding the mode of delivery.
Cesarean Section in Bahrain:
Al Hilal Hospital is the largest and fastest-growing chain of private healthcare providers in Bahrain, with five branches. Al Hilal Healthcare Group is committed to providing high-quality healthcare services at an affordable price to the people of Bahrain through a combination of superior medical technology and excellent clinical services. Its vision is to be the largest healthcare service provider in the region by catering to the needy at the most affordable rates.
The Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology has been providing comprehensive healthcare for women. As a result, the healthcare group has successfully given birth to new babies and new mothers through Cesarean Section with utmost care.
Cesarean Section Specialist in Bahrain:
Al Hilal Healthcare group is equipped with several well-qualified and experienced Gynecologists. In addition, the doctors have gifted motherhood and parenthood to the patients through Cesarean Section.


