Cervical cancer is the fourth most frequent cancer in women with an estimated 570,000 new cases in 2018 representing 6.6% of all female cancers.
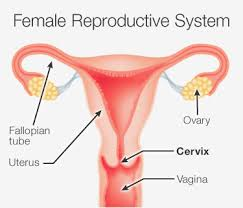
Cervical cancer happens when cells in the cervix grow in an uncontrolled way and build up to form a lump (also called a tumor). As the tumor grows, cells can eventually spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening. Your cervix is the lowest part of your uterus (or womb), and it is found at the top of your vagina.
Symptoms of cervical cancer tend may include:
irregular, intermenstrual (between periods) or
abnormal vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
back, leg or pelvic pain
fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite
vaginal discomfort
odorous discharge
The high mortality rate from cervical cancer globally could be reduced through a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, early diagnosis, effective screening and treatment programs.
Screening finds abnormal cells so they can be removed before they become cancer.
Cervical screening is for women and people with a cervix. Screening is offered every 3 years from age 25 to 49 and every 5 years from age 50 to 64. This is because most cervical cancers develop between these ages.
You should consider having screening regardless of your sexual orientation, sexual history, or whether you have had the HPV vaccination.
Pap Smear
Pap smear is a screening test that looks for abnormal cells in the cervix. It is quick and painless. Abnormal cells can develop into cancer if left untreated. The test involves using a soft brush to take a small sample of cells from the surface of your cervix. The sample is put into a small plastic container and sent to a laboratory.
It is tested for the types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer. If you have a negative result for the most common types of HPV that cause cervical cancer, your risk of cervical cancer is very low. If you have a positive result for HPV we will check the sample for abnormal cells. Abnormal cells are not cancer, but they could develop into cancer if left untreated.
HPV and cervical cancer: Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). Most people will get the virus at some point in their life. It is spread through close skin to skin contact during any type of sexual activity with a man or woman. HPV can stay in the body for many years. It can stay at very low or undetectable levels and not cause any problems. This means an HPV infection may have come from a partner a long time ago. There are many different types of HPV, but only some high-risk types can lead to cancer. The types of HPV that cause cervical cancer do not cause any symptoms. In most cases, your immune system can get rid of the virus without you ever knowing you had it. But sometimes, HPV can cause cells in your cervix to become abnormal, and the abnormal cells can go on to develop into cancer.
This mother’s day it is worthwhile to gift yourself and your mothers a pap test.
Get “Pap”ped this Mother’s day!!
BY:
MBBS,MS, MRCOG
Bahrain – Muharraq


